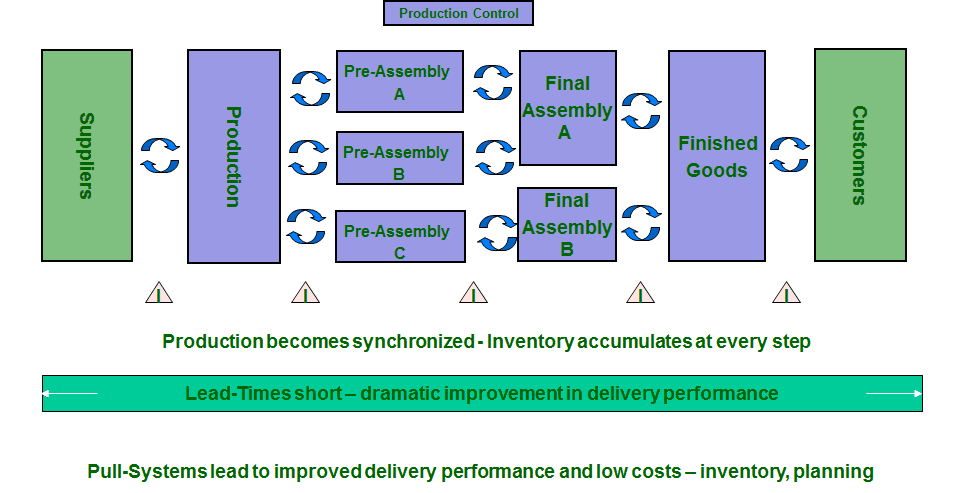
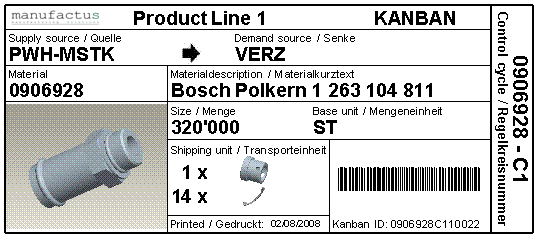
There are several typical scenarios for the usage of electronic kanban, where manual kanban systems reach their limits quickly.
Here are some typical examples where e-Kanban is inevitable:
- Management of many part numbers and Kanban cards
- No standardization of Kanban processes
- Lost Kanban cards
- Low transparency of open Kanban orders, stocks, etc.
- Employment of Kanban loops despite big distances (e.g. external suppliers)
- Fluctuating customer demand and single orders
- No real-time information about possible inventory shortages
- No possibilities for the analysis of historical data for the control and optimization of Kanban parameters
In the end with a manual Kanban system there exists almost no continuous improvement in order to achieve maximum possible savings => not a “living system”!
Electronic Kanban is a software support for traditional manual kanban systems.
Within manual Kanban systems the information (the signal) about the demand at a consumption stage is passed on by card, container or other types. This signal is passed on manually from the customer to the supplier.
With the e-Kanban System IKS the signals are mainly transmitted electronically. Each possible state of the signal (e.g. full, empty, in transport, etc) is being recorded and stored. The transmission of different states is takes place either manually by a user entering the data via keyboard or automatically via bar code reader. In this way each kind of unwanted time efforts or several types of waste will be eliminated efficiently.
An electronic Kanban system achieves the following goals:
- Kanban data management
- Increase of information transmission speed
- Increase of transparency
- Support of existing Kanban processes
- Continuous improvement of the Kanban system
The following table shows a huge number of advantages of an electronic Kanban system in comparison with a manual Kanban system:
| Manuel Kanban | Electronic Kanban |
| Mostly chaotic data management using Access, Excel or any other system, which is not built for Kanban | Data management in a robust system, especially designed for Kanban handling and movements |
| Frequently complicated printing of Kanban cards | Simple and fast printing of several different types of Kanban cards |
| Very difficult or impossible handling of larger numer of Kanban loops and cards | Simple and easy handling of thousands of Kanban loops and cards |
| Sending of Kanban signals over greater distances causes time loss, complications and faults | Automatic sending of up to date information worldwide and avoiding of non-added value activities |
| All faxes and emails must be sent by hand | Automatic sending of faxes and emails in the background |
| No support of necessary and repeating Kanban processes, e.g. automatic card printing, lost cards,… | Automatic support of necessary and repeating processes |
| Low transparency of current inventory and Kanban orders | Full transparency of current and actual inventory and Kanban orders |
| No “real-time” information about open Kanban orders | “Real-time” information about open orders and availability inventory e.g. through the electronic Kanban Board |
| No priority assignement for Kanban orders | Automatic priority assignment for Kanban orders, what is next in the pipeline… |
| No alarm in critical situations | automatic alarm signals and visuals at critical inventory situations and late deliveries |
| No tracking of historical inventory movements | Full visibility about historical inventory movements available in order to support inventory reductions and optimization |
| No tracking of actual delivery performance | Online availability of the current and of the historical delivery performance with several additional tools for analyzing the potential problems and improvement areas |
| Very difficult management of seasonal and variable demands | Automatic calculation of Kanbans needed, based on future demands and customer orders |
| Very difficult handling of products running out or starting up | Dimensioning of the Kanban loops can be automatically adjusted |
| Manual data transfer to the host system and no reporting | Connection to a host system, automated data transfer and simple access to standard reports |
LEAN / KANBAN
Click on the desired topic to learn more.
I am text block. Click edit button to change this text. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.